
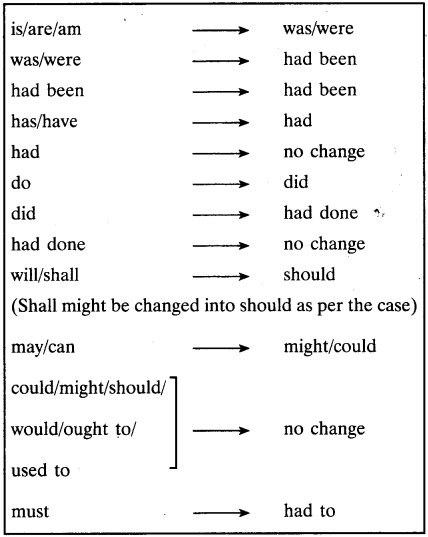
The First-person in direct speech becomes the subject in indirect speech. Modals like must, may, and can in direct speech become would have to/ had to, might, and could respectively in indirect speech. Simple future and future continuous tense in direct speech changes to the present conditional and conditional continuous tense in indirect speech. Simple present tense in direct speech will be in simple past in indirect or reported speech. Present perfect tense and present continuous tense in direct speech will be in the past perfect tense and past continuous tense in indirect or reported speech. If the reporting verb of the direct speech is in the past tense, all the present tenses used in direct speech will be in the past tense in the indirect or reported speech. We will use a reported clause (like, 'said,' 'asked,' 'replied') before the quotation. She said she would be at the playground on time.īasic Rules of Direct and Indirect Speech that Students of Class 10 Should Know Rules of Direct Speech for Class 10įor every character's speech, use separate lines.Īlways start a speech with a capital letter.Įvery speaker's speech should be in quotes ("XYZ"). She said, "I'll be at the playground on time." Indirect speech helps to learn to summarise someone's dialogue and thoughts adequately.Įxamples of Class 10 Direct and Indirect Speech Direct Speech Examples: Also, indirect speech follows past tense, generally.Įxample: Rahim said he was going to the playground.īenefits of Learning Direct and Indirect Speech for Class 10īoth direct and indirect speeches are essential parts of the English language.ĭirect speech helps to provide or quote an exact portrayal of the speaker and their moods and tone of speech. Indirect or reported speech refers to the speech that doesn't use the actual word-to-word statement of the speaker. This type of speech has the word-to-word restatement of the speaker's speech.Įxample: Rahim said, "I am going to the playground." Direct speech refers to the speech with the speaker's actual words.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
